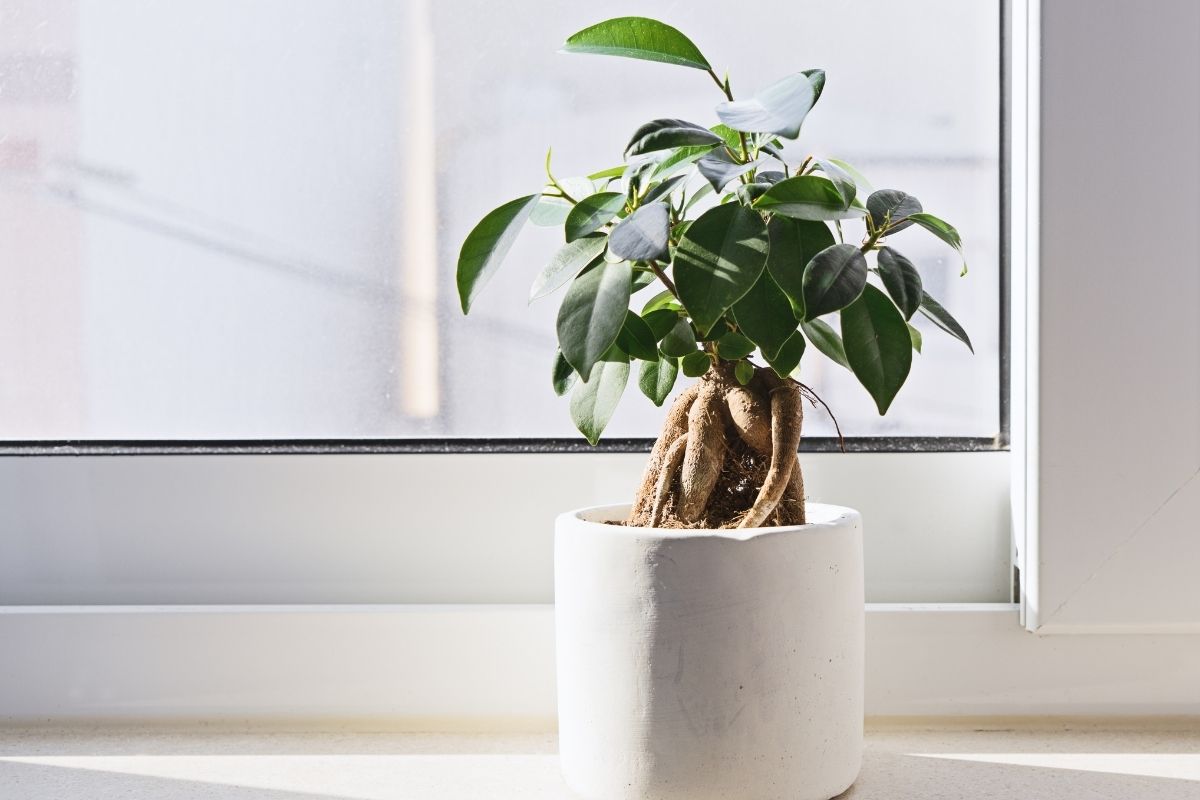
There is nothing quite so satisfying as cultivating an indoor bonsai tree. Just like watching new leaves on your indoor plants peek their shiny little heads out during the growing season, watching your growing bonsai trees take shape with structural pruning is the stuff that a bonsai enthusiast’s dreams are made of.
Fair warning: the art of growing and caring for a bonsai tree requires knowledge and experience in this craft.
As you get into bonsai gardening, you’ll realize that proper tools and training can help you start shaping your bonsai trees. Considering that the tree’s shape is a crucial aspect, there are several bonsai tree species and styles to use for your plant.
And that’s what I want to do here. I want to introduce you to the various bonsai tree care techniques so that you can become a bonsai gardener (a lifelong hobby) and start putting indoor bonsai masterpieces all around your home.
With a few plants, a set of tools, a suitable container, bonsai gardening skills, and plenty of TLC, your adorable miniature tree can add a touch of elegance and charm to your home.
bonsai tree care
The type of care you provide depends on the bonsai tree species that you are caring for. A deciduous tree (such as a ficus tree) requires different soil moisture levels than a coniferous bonsai tree (such as a juniper), which will inform what kind of soil mixture you use, how often you need maintenance pruning, and what kind of fertilizer to use.
watering
An important element in bonsai tree care is watering. You need to know the right amount of water that your plant needs since too little can dehydrate the tree while too much water can drown it (and cause root rot). The idea is to wait for the soil to begin drying out without allowing it to dry completely. Water the plant and allow water to seep out of the bottom portion of the pot. Never water your bonsai tree unless you have observed that the soil is beginning to dry out again.
Because the bonsai plant is in a small pot, its root system doesn’t have much space to grow (which is partly what keeps the bonsai plant so small). This is why your chosen growing medium is possibly more important than your watering schedule. Choosing the right soil mixture will allow growing bonsai trees space to grow and take up nutrients and water. When in doubt, you can always use a moisture meter to test the moisture levels before watering.
soil & fertilizer
Soil and fertilizer are perhaps the most important considerations when growing indoor bonsai trees. Bonsai plants rely on consistent watering (without over-watering) and one way to provide that is with a soil mixture that retains soil moisture. Because the miniature tree’s root system is sensitive to over-watering, you also want a soil mixture that allows good drainage. To get both the moisture retention as well as the drainage, a soil mixture of organic matter, Akadama, lava rocks, and pumice will work perfectly.
As for fertilizer, bonsai plants benefit most from an all natural slow release fertilizer. Unlike liquid fertilizers, the slow release fertilizer often comes in pellets, making them easy to sprinkle atop your rocky bonsai soil mix.

placement
Remember that a bonsai plant is basically a miniature tree. As such, it is expected to grow to the heights of the forest canopy, where it can catch all the sun’s rays all day long. When we grow indoor bonsai trees in tiny pots, we prevent the small tree from reaching the sun at the top of the canopy. Instead, we must provide that sunshine through proper placement. Bonsai plants are happiest next to South-facing windows, which receive a lot of sunlight. They like to be close to the window so that they receive warmth from the sun, which is important for optimal growth. If this isn’t an option for you, then grow lights may be helpful.
Depending on the bonsai tree species, you may want to also place the plant in a humidity tray. Many houseplants, including bonsai plants, originate from tropical climates. Maintaining relative humidity in the home can help make your plants feel welcome 🙂
pruning
Root and branch pruning is also important in maintaining the quality and appearance of your bonsai tree. The perfect time for root pruning is at the onset of spring, or when the roots of the plant are already established in the pot. You will need to choose the roots that you intend to keep, then eliminate the bad ones. Branch pruning, on the other hand, must be done just before spring starts. Select the branches that need to be pruned and kept, since the right pruning techniques are crucial to sculpting the tree into various shapes.
how to shape a bonsai tree
Bonsai is styled carefully and meticulously, so that the miniature appearance may be met. Styling is also evident in various practices, such as Niwaki and topiary. In bonsai gardening, you will have better control of every aspect of the tree when it is young since it is quite small and easy to improve on. With a greater scale of matured or full-sized trees, you may notice that styling is limited to shaping and pruning the exterior volume at least once during the growing season.
It is also ideal that you avoid pruning just within the canopy, as well as the art of forming or bending of separate branches. For bonsai trees that are intended for display purposes only, you can carefully consider every leaf or needle as you shape the small tree. Some go so far as wiring twigs and branches so that they take on specific shapes.
Here are the different methods for shaping bonsai trees.
1. leaf trimming
This important technique includes the selective way of removing leaves or needles from the branches of your bonsai tree. The most appealing technique in the design is to show the branches below several groups of needles or leaves. In various species, such as coniferous plants, leaves or needles that are projecting quite below the branches require to be trimmed off.
There are other coniferous species, though, where their branches hold needles from the tree’s trunk to the tip. Many of the needles are trimmed, so as to expose the shape of the bark and branch. Bud and needle trimming may also be applied to coniferous trees to promote the back-budding on older wood since this does not occur in most conifers.
Here’s a good video on the basics of Leaf Trimming
2. pruning
By pruning the roots, branches and trunk, your tree can achieve its miniature look, as well as the dwarfing of its foliage. Moreover, pruning is the initial step to take when you want to transform a plant specimen into a suitable item for bonsai gardening. In this step, the top portion of the trunk is removed to give the tree a more compact appeal. Then, several other branches are removed or shortened to meet your planned design for your tree.
Eventually, the art of pruning is not severe when performed during the latter part of a bonsai’s life, and this technique is only done for stimulating the growth on branches that are not pruned. Make sure you perform this technique correctly, since it helps increase branch ramification. Pruning the correct way can also prevent trees from dying or becoming weaker.
Here’s a great video on pruning Deciduous Bonsai Trees
3. wiring
Proper wiring is evident in most types of bonsai specimens. This is usually done by wrapping aluminum or copper wire around the plant’s trunks and branches, so you can create your preferred form and style. Wiring is also useful in making detailed placements of the leaves and branches. Wire securely holds all the branches in place until they are eventually converted or lignified into wood. In most instances, deciduous trees may take between 6 and 9 months, or perhaps even an entire growing season before their branches lignify.
On the other hand, this process may take longer for conifers, such as spruce and pine. You may also use wires to connect one branch to another branch or the pot, since the tightening action applies the right amount of force to branches. It is also important to note that there are species that may not lignify strongly and there are branches that can be too brittle or stiff. In this case, such a specimen is not recommended for wiring, so you may only shape it by pruning.
A video showing wiring a bonsai.
4. grafting
A bud or branch, or any other growing material, is placed in a prepared spot under the tree’s bark. Grafting is important because some species may not thrive well as miniature plants, so their trunks must be grafted onto a more stable root stock. Among the common species where grafting must be applied include the Japanese Black Pine and Red Maple tree. Another instance where grafting is important is when you want to add roots or branches to complete and enhance the overall bonsai design. Various grafting techniques that may be used include bud grafting, thread grafting and branch grafting.
Here is a great video walkthrough of grafting bonsai trees.
5. deadwood
There are some people who prefer to shape or improve the appearance of dead wood that aim to stimulate the maturity and age in bonsai trees. Jin is one of these techniques, and this is applied when the bark is removed from a branch to give an image of a piece of deadwood. Shari is another bonsai gardening technique that refers to the process of stripping bark from the truck’s areas.
This technique simulates the scarring of wood due to a strike of lightning or broken limb. Aside from stripping, the deadwood technique may include the application of lime sulfur or other chemicals for bleaching and preserving the deadwood.
6. defoliation
The dwarfing of the foliage may be done in some deciduous bonsai trees by complete or partial plant defoliation throughout the growing season. Be aware, though, that some species may not be able to survive this bonsai technique. When you defoliate a tree, most of its leaves are clipped along the petiole of the leaf.
Eventually, these petioles become dry and fall off. The tree soon produces a newer crop with smaller leaves, which may be half the width and length of the original crop. The smaller size of the leaves adds to the aesthetic of dwarfing the tree. However, the process of defoliation may weaken the bonsai tree, so this technique must never be done in two consecutive years to prevent the plant from dying.
7. clamping
For larger plants or those with stiff and brittle wood, the use of clamps is ideal for shaping branches and trunks. Clamping is done by straightening or bending a part of the tree with greater force, which wiring can never provide. You can prevent damages to the plant by tightening the clamps gently and making changes over several months or years.
Here’s a helpful video on a clamping technique
understanding the proper care of bonsai trees
Miniature plants or trees such as bonsai must be given specialized care and attention to help them grow beautifully over time. As compared to regular houseplants that you use in container gardening, tree species that normally thrive in forests or the outdoors grow long roots with structures that will require liters of soil. A bonsai container, however, is less than 25 centimeters in length, and it can hold up to 10 liters of soil. Aside from the roots, the leaves and branches of these trees are much larger, and they may grow up to a height of 5 meters or even higher in some species.
On the contrary, the largest bonsai height does not go over 1 meter, and several specimens are quite small. These varieties in sizes tend to affect the plant’s transpiration, pest resistance, maturation and nutrition. With this in mind, it is important that you provide intensive and essential methods for growing these trees.
The right amount of water must be provided to your plant, and this depends on the species of your bonsai tree. Some trees require wet, moist or even dry soil, so you should be aware of these aspects when watering it. You should also understand that repotting must be done at certain intervals, depending on the age and strength of the tree.
As with regular houseplants, the application of fertilizer is important to ensure its great condition and health. Make sure you choose the right soil that fits the needs of your plant, such as one with fast-draining and loose quality. Then, apply the appropriate amount of fertilizer as required for your specimen.
Lastly, outdoor bonsai trees must be protected from overwintering, as this can cause serious damages to your plant. It is also necessary that you provide the right lighting condition and temperature for your plant, and avoid placing the plant inside the house. Only a few species can thrive indoors since the climate is usually dry. So, make sure you place it outdoors most of the time to maintain its health and amazing appearance.
aesthetics of bonsai trees
Primarily, aesthetics refer to the characteristics and principles of Japanese tradition when it comes to the art of making miniature potted trees. A number of cultural characteristics in Japan is influenced by the Zen school of Buddhism, including the expression of wabi-sabi, which has guidelines for the bonsai tradition applied in that culture. Additionally, several cultures all over the world have implemented the Japanese approach in bonsai gardening, and there are some other variations that have appeared. These new variations are based close to the original aesthetic philosophies in the Japanese tradition.
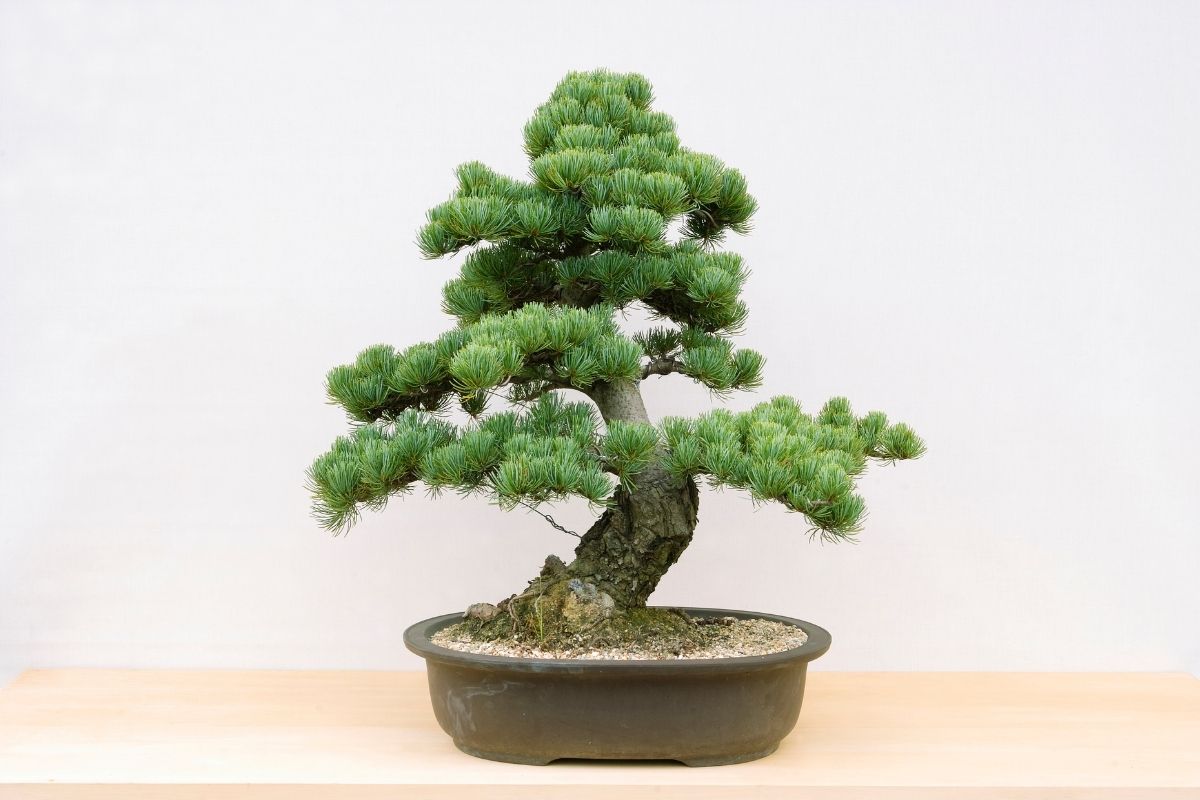
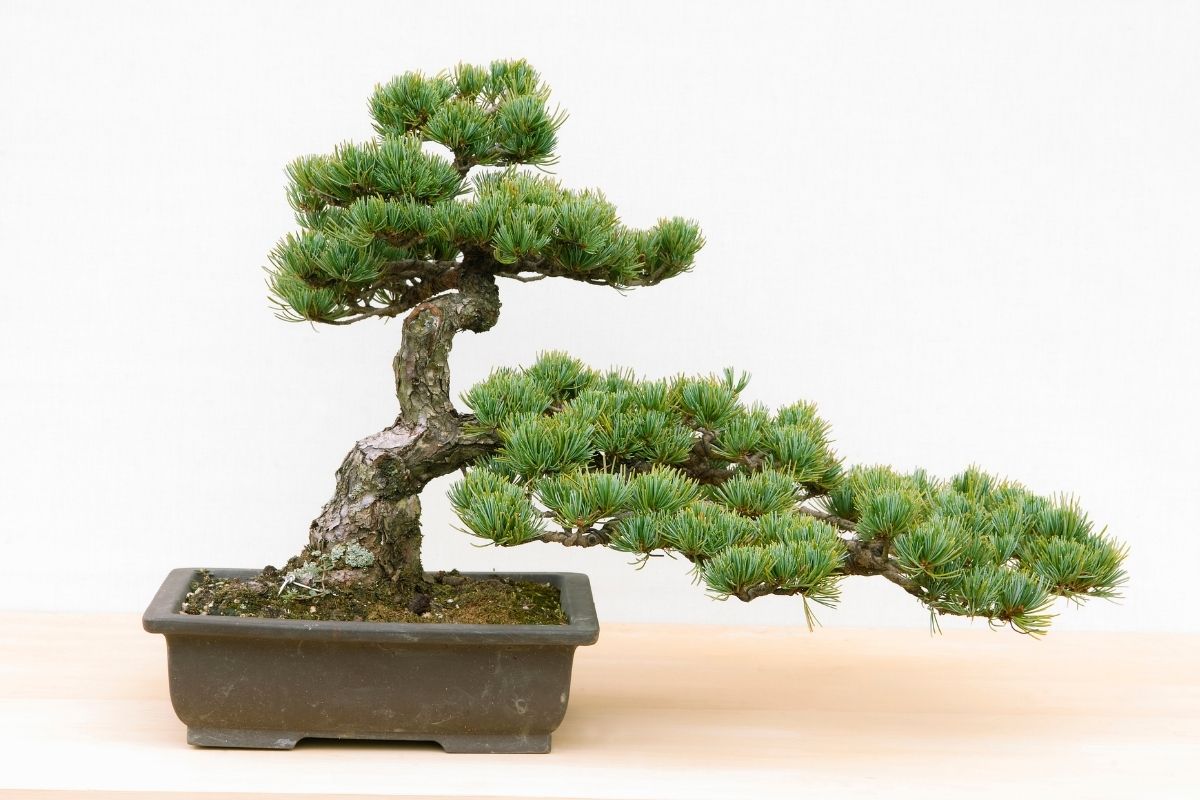
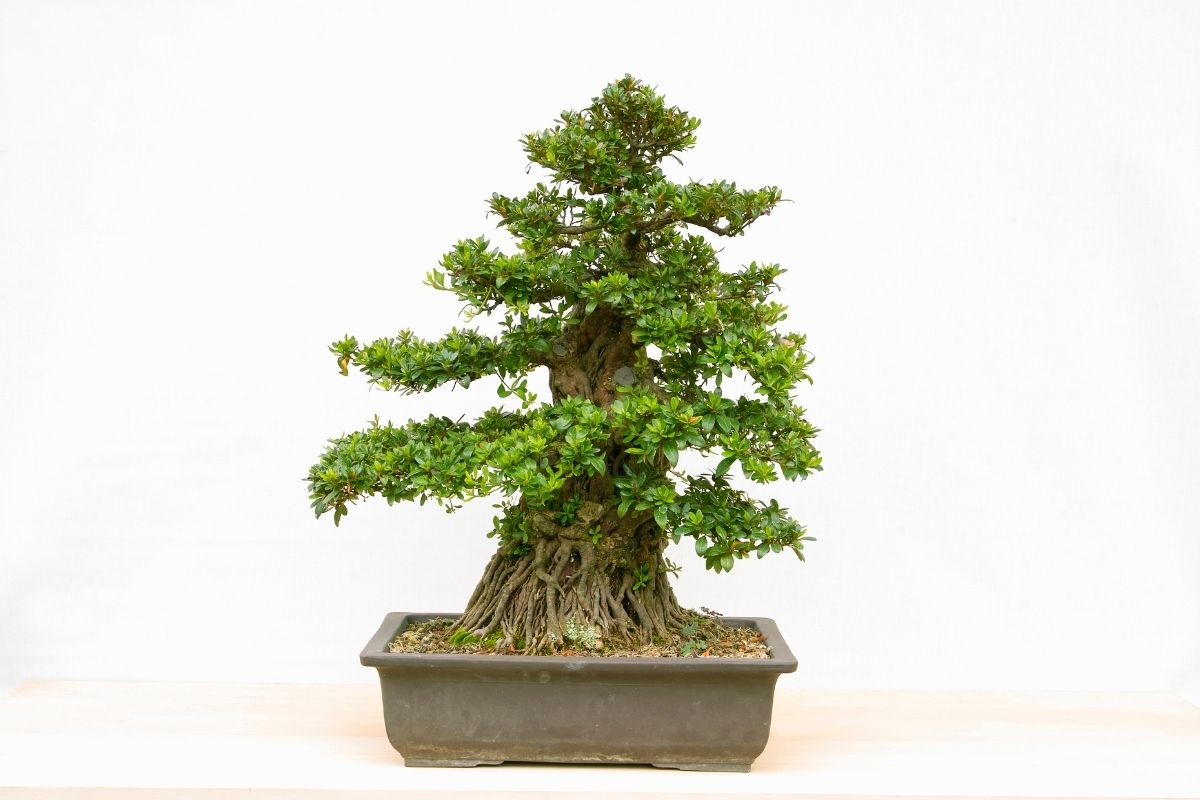
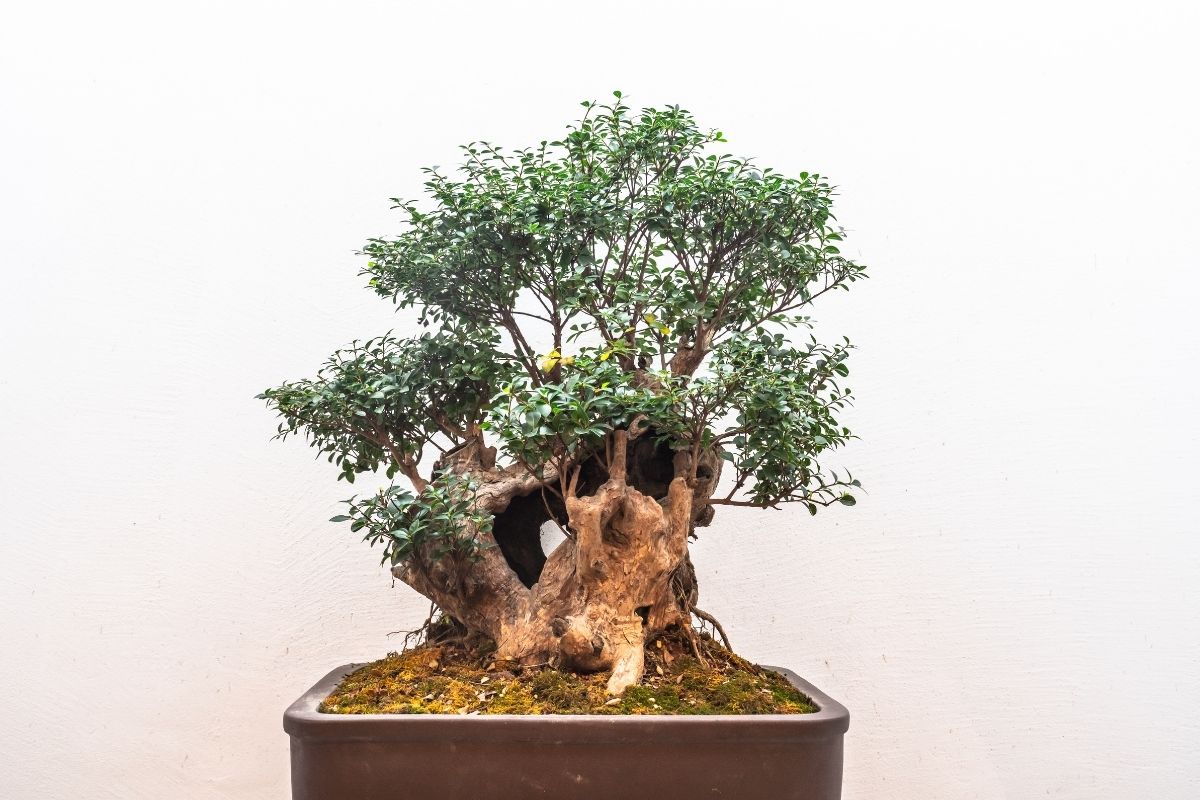







The different guidelines applied in the art of growing bonsai trees assist practitioners as they work and follow an established tradition. Although the implementation of these guidelines do not automatically guarantee perfect results, these rules in aesthetics may be altered without affecting the bonsai specimen negatively. Among the typical bonsai aesthetics are the following:
- Poignancy. Most of the established rules of bonsai cultivation guide practitioners in creating a tree that depicts Wabi-sabi (acceptance of imperfection or transience), as well as a portrayal of the mono not aware (empathy toward the passing of things).
- Proportion. The most recognized proportions among different elements mimic the appearance of a mature tree. Small trees that have needles or leaves that are out of proportion are generally avoided.
- Asymmetry. Bilateral or strict radial symmetry found in root placement or branches are not accepted in bonsai aesthetics.
- Miniaturization. This refers to the process of keeping the tree small enough so it can be grown into a container while maintaining its mature and full-grown appearance.
- No Trace of the Artist. There should be no traces of the person’s touch on the tree. Hence, any scars made when the branch is removed from the tree must be hidden completely. It is also important that any wiring is removed or concealed, and no permanent marks must be left on the bark or branch.
types of bonsai trees
There are a lot of tree species that work well for bonsai styles. Here are some of my favorites:
- juniper bonsai
- banksia trees
- ficus bonsai
- Chinese elm bonsai
- jade bonsai
- Fukien tea bonsai
- bonsai palm tree
- pomegranate bonsai
- red maple bonsai
- Japanese black pine bonsai
- trident maple bonsai
popular bonsai styles
Bonsai trees are styled in various ways, such as slanting, cascading, raft, formal upright, or literati. There are also some other forms that are not as popular to the public, including split-trunk, driftwood, weeping, and windswept. These styles are usually used to describe the orientation and appearance of the plant’s main trunk. Each style is presented below.
1. cascade style (Kengai)
In this style, specimens are styled to resemble trees that are found along the sides of the mountains or over water. The tip of the plant may also be presented in a semi-cascade style where it extends just a little beneath the edges of the bonsai container.
2. slant style (Shakan)
Bonsai trees that depict the slant style have straight trunks that are similar to those grown using the formal upright style. The main difference, though, is that the slant style has the trunk emerging from the soil at a certain angle. Moreover, the tip of the bonsai is found at the right or left of the root base.
3. formal upright style (Chokkan)
As the name suggests, it has an upright and tapering trunk. There is also a regular progression of branches, where they are arranged with the broadest and thickest at the bottom part, while the shortest and finest at the top.
4. informal upright style (Moyogi)
This bonsai style features curves in branches and trunk while the apex is found on top of the trunk’s entry and into the soil line.
5. raft style (Netsuranari)
It resembles a natural phenomenon that causes a tree to topple onto one side due to erosion, for instance. The tree’s branches found at the top of the trunk continue to grow into new groups of trunks.
6. shari style (Sharimiki)
The style portrays a tree as struggling to live while there is a large portion of its trunk that does not have any bark left.
7. forest style (Yose Ue)
In a single bonsai container, different trees of similar species are planted (usually an odd number).
8. multi-trunk style (Ikadabuki)
This is quite an interesting style since it presents a tree with all its trunks growing in a single spot with just one root system.
Other styles include the literati (bunjin-gi), which shows a bare trunk line and reduced number of branches, as well as foliage positioned on top of the contorted trunk. Windswept (fukinagashi) is another style, and this presents a tree as though it is affected negatively by strong winds that blow from one direction. This natural phenomenon is believed to shape the tree on a shoreline or on top of a mountain ridge.
tools used in bonsai gardening
If you are a beginner in bonsai gardening, it is important that you have the necessary tools and equipment to perform this task the right way. Certain tools can help you get the job done without causing any damages to the tree.
A basic bonsai tool kit includes
- wire cutters,
- small nail scissors for detailed work,
- secateurs (by-pass type),
- wire cutters
- and a pointed long piece of wood such as a chopstick for combing out the roots with care.
When you buy your tools for Bonsai gardening, you may decide to purchase these individually or look for a small kit with all the important tools included. Costs tend to vary significantly, but it is common sense that you buy good quality tools within your preferred budget. Cheaper tools made of low-quality materials and poorly constructed may only deteriorate quickly. In case cheap scissors lose their edges, you will need to sharpen them frequently, and this can take a huge amount of your time.
Something like this would be great for getting started:
It is important that your tools are placed in a specific container where you can find them easily. Furthermore, you should make it a point to keep your tools well-maintained and clean. Regular sharpening is necessary for your cutting tools, as this practice can increase their life and durability. Dirty and blunt tools are also incapable of cutting through the wood, and they may end up crushing the wood rather than cutting them properly.
Since plant sap may collect on the blades of cutting tools easily, you should remove it with an abrasive paper or wire brush. Otherwise, the blades may appear black and affect the overall quality of your scissors.
Among the basic tools that you need to prepare for bonsai gardening, include the following:
- Bonsai scissors (long-handled) – used for detailed and fine leaf or shoot work. It is essential to keep them razor-sharp at all times to ensure the finest cut.
- Side or Knob cutter – cuts away branches while leaving a small indentation to cause the wound to heal flat. Those with narrower blades can cut through wood of varied strength.
- Jin pliers – strips away wood fibers when you want to create a jin from the tree’s branch.
- Wire cutter – cuts cleanly through any wire that is close to the bark while preventing damages.
- Draw knife – also referred to as the bark-stripper. This tool can strip away back from wood easily.
In addition to these basic tools, you will need a black turntable that allows the easy turning of the bonsai as they are being worked on. You should also include a bottle of petroleum jelly in your toolbox, as this can be applied to fresh wounds of Spruce, Larch, Pine, and other resinous trees that tend to bleed heavily. Instead of using a conventional wound sealant for bonsai, petroleum jelly can be an excellent alternative.
You will also need soil sieves when you re-pot your plants, as this can help remove dust and other fine particles from getting into your mixed bonsai soil. If you wish, you may use root hooks for removing or combing out old soil. However, you may also use a chopstick or your hands to prevent serious damages when potting on or re-potting your bonsai specimen.
Wire is also used in bonsai gardening, as this ensures the accurate positioning and shaping of trunks and branches. This tool is also useful for anchoring in drainage mesh and newly potted bonsai trees. Although Japanese originally used copper wire because of its superb holding capacity, it is now less popular and difficult to source commercially. As an alternative, you can find customized aluminum wire from major bonsai outlets or garden centers. Invest in at least three different gauge wires that can be used for shaping different types of trunk and branch thickness. Initially, you may buy 1-mm, 1.5-mm, and 2-mm gauge wires that will come in handy during your gardening.
bonsai tree display
The display features one or a few bonsai specimens in a manner that gives viewers an opportunity to observe and discover the key features of the tree from the best position. This position presents the tree’s defined front side, and this is designed into all the bonsai on display. It also positions the tree at a certain height that gives viewers a chance to visualize the bonsai specimen as a mature tree seen from a certain angle and distance.
The position of the bonsai must not be very low so that the viewer tends to appear as though he is hovering uncomfortably in the sky. Moreover, the height must not be too high that viewers may seem to be looking way up the tree from the ground. Instead, bonsai trees should be displayed as if they are in an art gallery, which is in isolation, at an appropriate height, and against a plain backdrop. The tree should also lack redundancies, including accessories and labels.
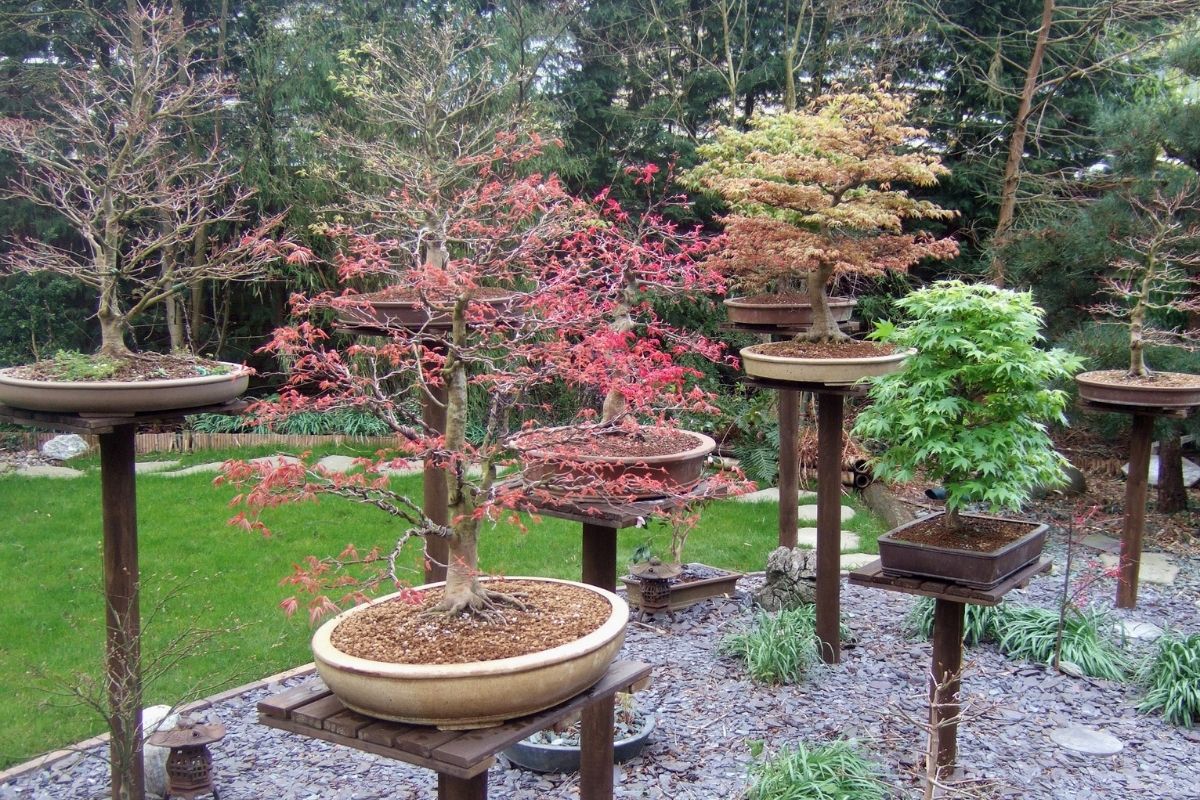
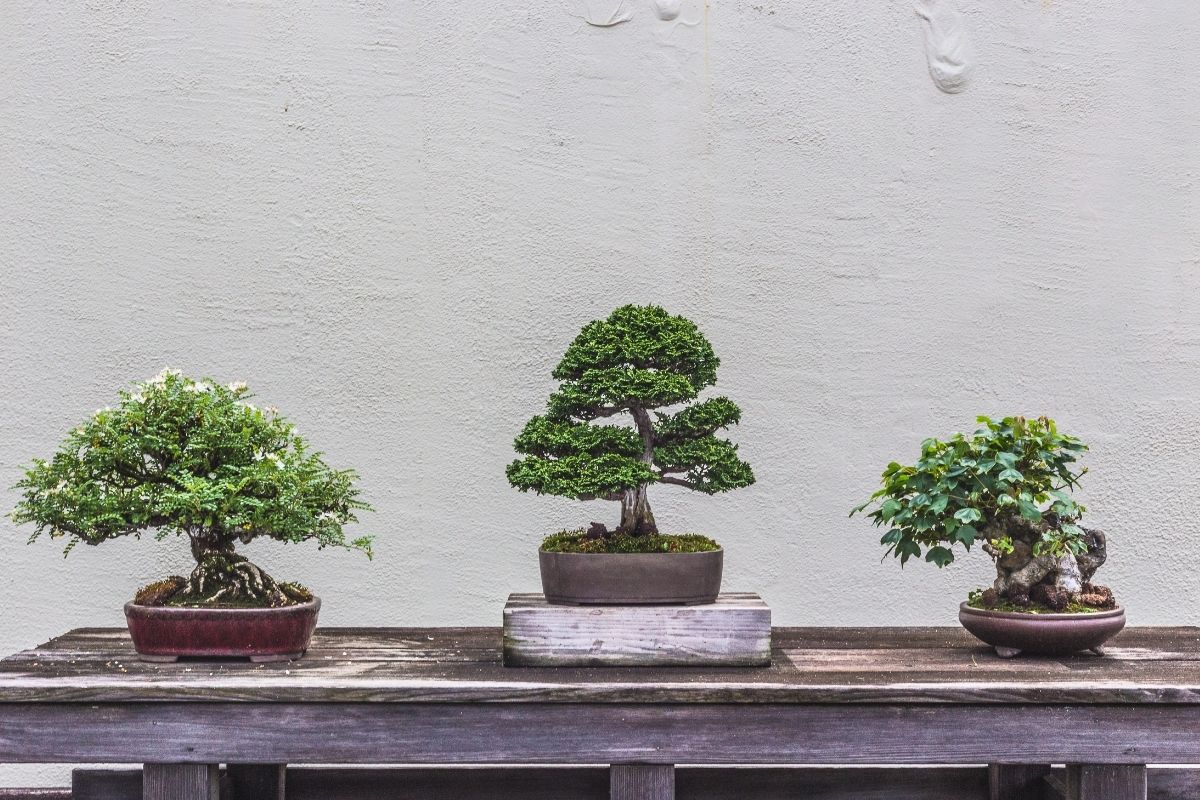
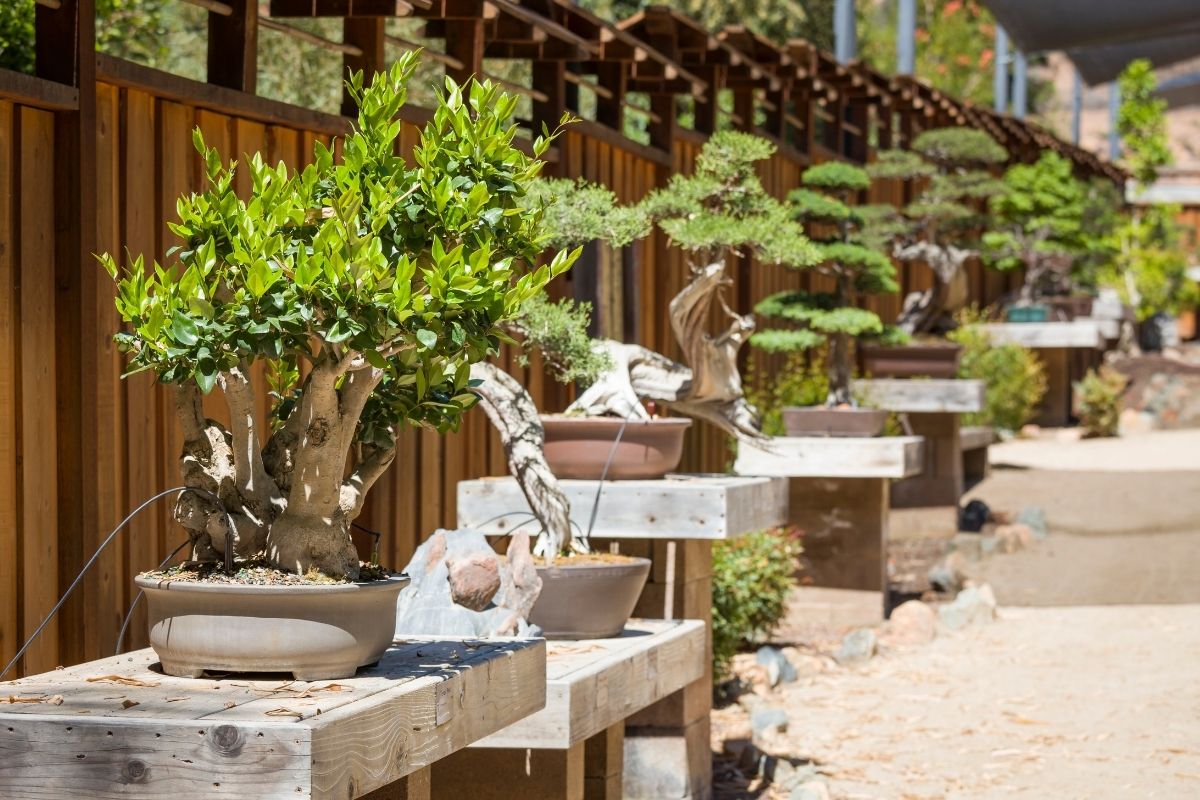




If the tree is meant to be displayed outdoors, there are certain aesthetic rules to keep in mind. In most instances, outdoor bonsai displays are rarely permanent, and these trees are in place only for a few weeks or months at a specific time. The best way to avoid any damages on the trees is to make sure that the outdoor display will not prevent the amount of sunlight required for these trees on display. There should also be certain tools that can block precipitation or excessive wind to ensure their excellent condition.
Because of various natural constraints, outdoor bonsai displays appear to be quite rustic in style, with stone or wood components. A typical design available is the bench, and there may be a few sections featured at varying heights to complement the different sizes of the trees. When there is sufficient space, outdoor displays have big spacing, so viewers can concentrate on observing each piece one tree at a time. On the other hand, trees that are crowded or placed too close together may confuse the viewer. It can also lead to aesthetic discord that occurs in adjacent trees that comes in different styles and sizes.
Exhibition bonsai displays provide a certain number of trees to be presented in an exhibit format. They are also positioned indoors, which is typical in bonsai design competitions. To make sure that many trees are positioned close to each other, displays may use a particular sequence of small alcoves where each contains a pot and its specific bonsai details. Dividers or walls are placed between alcoves, so it is much easier for people to view just one bonsai tree at a time. It is also common that the back part of the alcove has a neutral pattern or color, as this can prevent any distractions to the viewer. Finally, the bonsai pot is positioned securely on a formal stand with a design and size that matches the bonsai and its container.
When placed indoors a formal display of bonsai specimens is arranged in a way that can represent a landscape. It also consists of the highlighted bonsai tree that is placed in a suitable container on top of a wooden stand. Accompanying this featured specimen is its companion plant (shitakusa) that represents the foreground. A hanging scroll may be used as its backdrop to enhance the plant’s beauty. These three important elements are selected to blend in harmony with each other depending on the season when they are displayed. Generally, indoor displays are quite temporary, which may last for only a day or two since most bonsai specimens can be intolerant of dry indoor conditions.
containers used in bonsai trees
You can find a number of containers that may be used for your bonsai specimen during its development. In fact, you may also return trees that are already planted formally in a bonsai pot to their growing boxes whenever necessary. A large growing container is ideal for holding several plants, and it offers a greater volume of soil for each tree.
This also encourages proper root growth that serves as a foundation for the specimen. Training boxes usually have one specimen and less volume of soil to condition the plant to the actual shape and size of a formal bonsai pot. Basically, there are no aesthetic rules followed for development containers, so you can choose any size, shape or material that will suit your preference.
Full-grown or mature bonsai trees are placed in formal containers that are typically ceramic pots. The design and style depends on what complements the tree, and you can choose from unglazed or glazed containers. Unlike most types of regular plant pots, bonsai containers have drainage holes in the bottom portion.
This feature works well with the fast-draining type of soil used in bonsai gardening, and it allows excess moisture to flow freely from the pot. If you wish, you may cover these holes using a thin screen to prevent soil from coming out. A good screening can also discourage pests from getting into the container. These pots also have vertical sides that allow you to remove the specimen’s root mass easily for pruning, replanting and inspection, although other container shapes may also be useful.
If you are not fond of using a traditional ceramic pot, you may opt for other types of container for your plant. For instance, there are multi-tree bonsai trees that may be made on top of a flat slab of large rock, and soil is usually mounted above its surface to make sure that the trees are planted within the elevated soil.
There are also modern styles where bonsai artists fabricated slabs that look like rock by using raw materials such as glass-reinforced plastic or concrete. These surfaces are much lighter and may contain pockets for water drainage or additional soil. Although there are other types of unconventional containers to choose from, ceramic bonsai containers are preferred in formal displays or competitions.
Bonsai trees presented in their mature state are housed in a pot shape, size or color that complements their structure and appearance. A suitable picture frame or scroll is also used as a background when these plants are displayed. Typically, containers that have sharp corners and straight sides are used for plants with formal styles, while round or oval pots are preferred for trees with informal designs.
Evergreen bonsai trees are also planted in unglazed ceramic pots, and deciduous ones come in glazed containers. Lastly, the trunk’s thickness, height and overall appearance of the tree determine the size and design of the container to be used.
bottom line
To ensure the visual appeal and good condition of your bonsai tree, you must make sure that it receives the right combination of soil, air, water, sunshine and fertilizer. You should also make sure that the plant is placed in a suitable environment to prevent it from drying out or withering during its early development. While this type of gardening may require your time, patience, and practical knowledge of this hobby, growing and caring for your own bonsai tree can be quite a rewarding experience.
More How To Guides
- How To Get Rid Of Scale On Plants
- DIY Terrarium Table: How To Make A Table With Plants Inside
- How to Use Leca for Plants: Step-by-Step Guide with Pictures
- How To Use Grow Lights For Indoor Plants
- How To Propagate Peperomia Plants 2 Ways
- DIY Propagation Box With Grow Light
- How To Make Pothos Fuller (In 5 Minutes)
- How to Make a Moss Pole for Your Climbing Plants
- How to Make Potting Soil for Indoor Plants, Plus My Secret Ingredient
- How to Propagate a Split-Leaf Philodendron: Easy Step-by-Step Guide